The optimum range of hole size for blast hole drilling with DTH is 90 mm to 254 mm (3 ½”–10″). Smaller blast holes are generally drilled using tophammer, and larger holes generally use rotary machines.
In other applications, like foundation drilling, DTH hammers can be used with single bit in hole sizes up to . 750 mm (30″). With multiple hammer units CD (Cluster drills) drill holes up to 70″ or 1778 mm.
As a rule of thumb, the smallest hole diameter a DTH hammer can drill is its nominal size. A 4 inch hammer will drill a 4 inch (102 mm) hole. The limiting factor is the outside diameter of the hammer, because, as hole diameter reduces, airflow is restricted. Maximum hole size for production drilling is the nominal hammer size plus 1 inch, so for a 4 inch hammer the maximum hole size is 5 inch (127–130 mm).
Choosing the right hammer is largely determined by hole size and type of rock formation. Ideally, the size of the hammer should match the required hole dimension as closely as possible, leaving just enough space for cuttings to evacuate the hole.
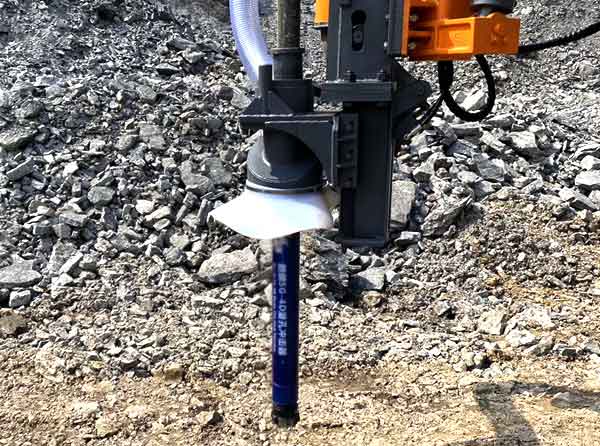


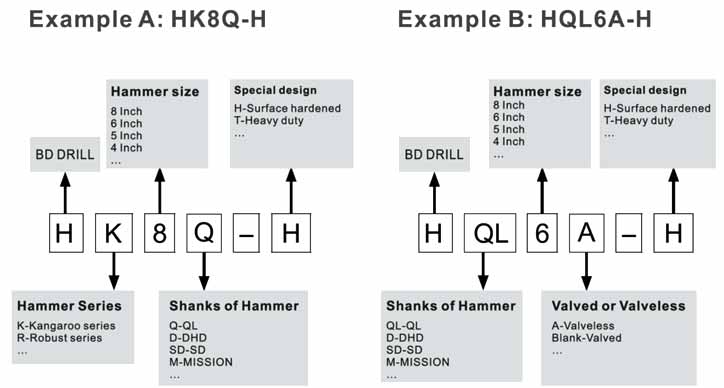
Product codes are a valuable tool to describe and identify the product. In the code structure we have tried to describe the product features with an alphanumeric system and not always 100% logical, but with the attached key you will be able to find the product you are looking for or alternative products.
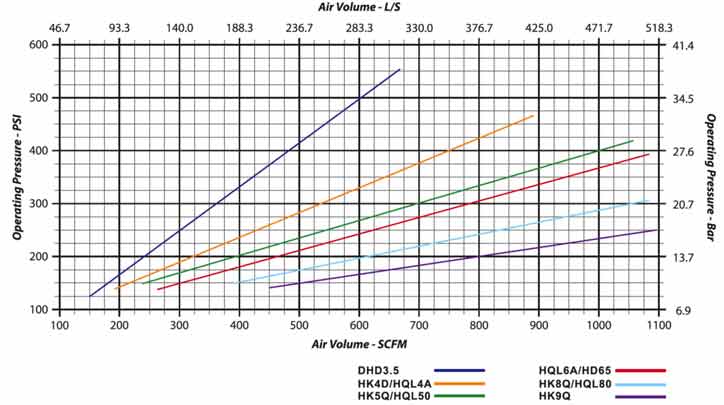
| Hammer | BR2A | DHD3.5 | HK4D | HD45 | HQL4A | HQL50 | HK5Q | HD55 | HQL60 | HQL6A | HQL80 | HD85 | HK9Q | HSD10 | HSD12 | HK12Y | N125-R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended bit size, mm | 76 | 92-105 | 112-127 | 140-152 | 165-178 | 203-229 | 216-229 | 245-305 | 305-445 | 305-350 | 305-445 | ||||||
| Bit Shank | BR2A | DHD3.5 | DHD340A | QL40 | QL50 | DHD350 | QL60 | QL80 | DHD380 | QL80 | SD10 | SD12 | HY12 | NUMA125R | |||
| External diameter, mm | 63 | 82 | 100 | 100 | 101 | 126.5 | 127.5 | 126.5 | 148 | 146 | 185 | 185 | 203 | 225 | 275 | 275 | 275 |
| Length excl. thread, mm (Less bit) | 837 | 855 | 915 | 1032.5 | 1057 | 1147 | 935 | 1167 | 1121 | 1182 | 1471 | 1487 | 1345 | 1413 | 1680 | 1590 | 1812 |
| Hammer weight, kg (Less bit) | 14.1 | 25 | 37.5 | 40.6 | 41 | 71.6 | 67.6 | 77.2 | 105 | 105 | 203 | 206 | 228 | 303 | 526 | 510.2 | 546 |
| Package case size | (L)910 (W)90 (H)120 | (L)1200 (W)110 (H)140 | (L)1010 (W)130 (H)160 | (L)1080 (W)125 (H)134 | (L)1150 (W)130 (H)160 | (L)1290 (W)150 (H)175 | (L)1100 (W)155 (H)180 | (L)1290 (W)150 (H)175 | (L)1270 (W)170 (H)200 | (L)1260 (W)180 (H)200 | (L)1440 (W)230 (H)270 | (L)1560 (W)230 (H)270 | (L)1500 (W)240 (H)280 | (L)1620 (W)275 (H)290 | (L)1880 (W)320 (H)320 | (L)1665 (W)320 (H)360 | (L)1880 (W)310 (H)310 |
| Top Sub thread | RD50 | 2-3/8″ API REG | 3-1/2″ API REG | 4-1/2″ API REG | 6-5/8″ API REG | 6-5/8″ API REG 7-5/8″ API REG | 6-5/8″ API REG | ||||||||||
| Working Pressure, PSI | 80-170 | 150-250 | 200-300 | 250-350 | 300-350 | 300-380 | 300-380 | 150-350 | 200-350 | ||||||||
| Air consumption, CFM | 250-350 | 300-400 | 500-700 | 500-800 | 600-900 | 950-1200 | 950-1200 | 1000-1800 | 1200-1500 | 800-1800 | |||||||
| Piston diameter, mm | 42.7 | 65 | 82 | 80 | 80 | 104 | 102 | 100 | 122 | 121 | 150 | 150 | 165 | 185 | 225 | ||
| Piston weight, kg | 1.7 | 5.1 | 9.2 | 9 | 9 | 17 | 17 | 16 | 24 | 24 | 38 | 42 | 50 | 68 | 110 | 111 | 111 |
| Wrench flat, mm | L47 W50 | L57 W35 | L74.5 W45 | L64 W40 | NO wrench flat | L89 W60 | L88 W50 | L89 W60 | L101 W65 | L101 W60 | L128 W70 | L140 W70 | L128 W70 | L140 W70 | L140 W70 | L140 W70 | L140 L70 |
| Feed force, kN | 2~6 | 3~8 | 5~15 | 6~25 | 7~20 | 10~25 | 15~30 | 20~35 | |||||||||
| Rotation speed, r/min | 30-70 | 3-90 | 25-80 | 20-70 | 25-60 | 20-60 | 15-35 | ||||||||||
| Drilling conditions and project specifications may require larger air package to be used | |||||||||||||||||
The DTH drill pipe consist of pipe and two adapters, box and pin. We use high strength and well-resistance alloy steel, inserting of high tensile seamless pipe, and according to different drilling depth, we can offer various thickness of pipe and material for customers’requirements.


DTH drill pipe Feature
• Diameter: 76mm, 89mm, 102mm, 114mm, 127mm, 140mm
• Length: 1000mm, 1500mm, 2000mm, 3000mm, 5000mm, 6000mm
• Thread: 2 3/8’’ API REG, 2 7/8’’ API REG, 3 1/2’’ API REG, 4 1/2’’ API REG,2 3/8″ API IF, 3 1/2″ API IF; BECO 6”, BECO 8”
• Wall thickness: 5.5mm/6.5mm/7.5mm/8.5mm/10mm
• Other spaecial size can be customized by customer’s drawing.
• Advanced heat treatment technology and friction welding mahcine.


| Rod dia | Rod length | Thickness | Connect thread | Wrench flats | |
| (inch) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | |
| 3 | 76 | 1000-6000 | 5 | API2 3/8”REG | 57/64.5 |
| 3 | 76 | 1000-9000 | 8 | API2 3/8”REG | 57/64.5 |
| 3 1/2 | 89 | 1000-6000 | 6 | API2 3/8”REG | 70/64 |
| 3 1/2 | 89 | 1000-9600 | 8 | API2 3/8”REG | 70/64 |
| 4 | 102 | 1000-9000 | 10 | API2 3/7”REG | 76/89 |
| 4 1/2 | 114 | 1500-7620 | 6 | API3 1/2”REG | 89/95 |
| 4 1/2 | 114 | 1500-9140 | 8 | API3 1/2”REG | 89/95 |
| 4 1/2 | 114 | 1500-9140 | 10 | API3 1/2”REG | 89/95 |
| 4 1/2 | 114 | 1500-9140 | 18 | API3 1/2”REG | 89/95 |
| 5 | 127 | 1500-9500 | 12 | API3 1/2”REG | 89 |
| 5 | 127 | 1500-9500 | 14 | API3 1/2”REG | 89 |
| 5 | 127 | 1500-9500 | 18 | API3 1/2”REG | 89 |
| 5 1/2 | 140 | 1500-9500 | 9 | API4 1/2”REG or 4’FH | 114 |
| 5 1/2 | 140 | 1500-9500 | 10 | API4 1/2”REG or 4’FH | 114 |
| 5 1/2 | 140 | 1500-9500 | 12 | API4 1/2”REG or 4’FH | 114 |
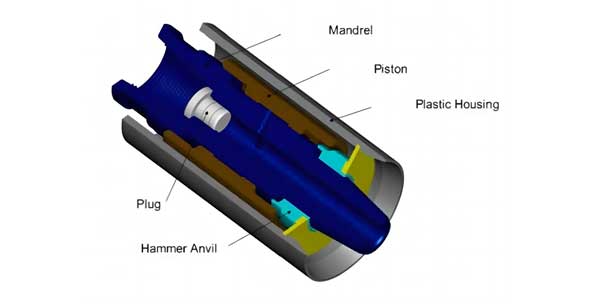
In case of jamming of any drilling tool in the boring process, the back hammer will assist you to solve the stuck problem by giving a backward impact power.
The back hammer may be mounted on the drill pipe joint between the borehole gripper and the swivel head, thus creating a combined effect of effective reverse impact and vibration.
The back hammer is consisted of three components and a plastic housing.

The housing acts both as an exhaust emissions guider and a muffler. With regards to the maintenance, it’s only necessary to keep it clean and the linking section we protected when the back hammer is not in use.
Our products are widely used in open-pit or underground mining, hydraulic engineering, bridge engineering, construction engineering, geotechnical engineering.

Oil gas drilling and other field. Our main products include DTH (down-the-hole) hammers and bits with capacity of drilling holes from 64mm–1020mm in diameter, DTH drilling tools with large diameter for deep hole drilling, eccentric casing system (ODEX) and concentric casing system, reserve circulation hammers and bits, drilling rig, rock drilling accessories and other relative equipment. With strong technical strength, we are making effort to create the best brand of Chinese drilling tools, and to be the top manufacturer in the world.

Accurate sampling;
Environmental operation;
Compared with conventional drilling tools, RC tools flush cuttings inside the pipe with small resistance to effect easy flushing;
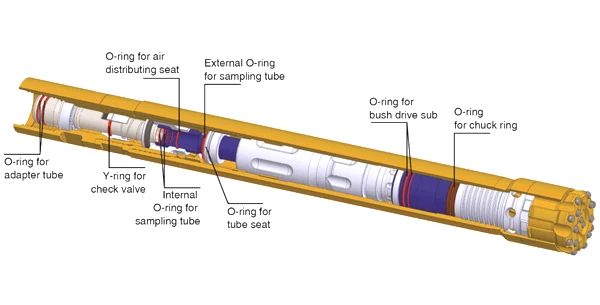
Special custom made alloy steel is adopted for sampling tube and shroud, and the surface of flushing pipe is hardened;
Good quality sealing rings are selected as follows:
A drilling system that flushes cuttings out from inside the pipe; Low air consumption; Drilling depth no more than 600m;Each bit should be matched with corresponding shroud.
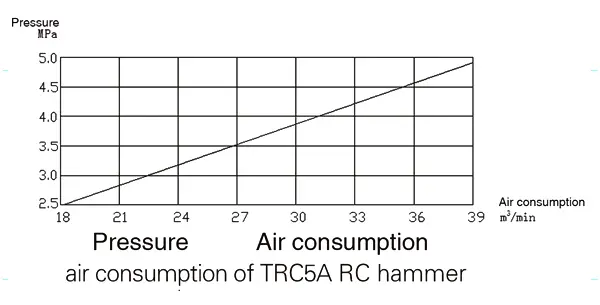
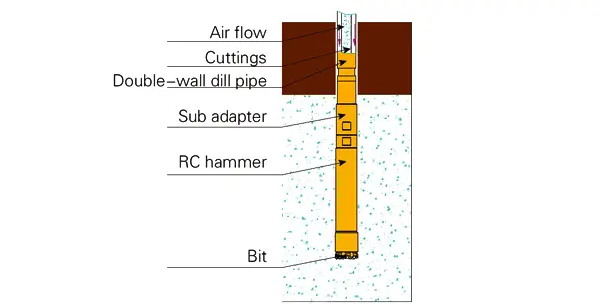
Compressed air flows into the annular space of the double-wall drill pipe, then into the inner pipe from the drilling tools in the bottom of hole, and carries cuttings out to the ground through the inner pipe.
RC tools are used in geological exploration, water well drilling etc


| Model | Rec.hole size(mm) | Thread connetion | Outer diameter(mm) | Length without bit(mm) | Weight(kg) |
| TH1080RC | 115-130 | REMET3.5” | 108 | 1145 | 50 |
| TH1162RC | 124-146 | METZKE4.0″ | 116 | 1191 | 61 |
| TH1186RC | 126-146 | REMET4.0″ | 118 | 1210 | 64 |
| TH1214RC | 130-146 | METZKE4.0″ | 121 | 1234 | 73 |
| TH1261RC | 135-152 | REMET4.5″ | 126 | 1272 | 68 |
| TH1305RC | 140-165 | REMET4.5” | 130 | 1294 | 82 |
| TH0820RC | 203-254 | REMET4.5″ | 188 | 1415 | 210 |
| TH12JORC | 305-450 | API85/8”REG | 280 | 1869.5 | 590 |
Notice: There is a chance that SHANDIKE may make changes on above-mentioned information. Product pictures and parameters about models, data, performances and specifications on this website are for reference only.
The RC bits are the tool cutting rock. SHANDIKE RC DTH bits are made of superior quality alloy steel and T.C carbides.

1. Reverse Circulation Technology
– Utilizes a unique air/fluid circulation system that transports cuttings upward through the center of the drill string, ensuring clean and uncontaminated samples.
– Minimizes hole deviation and improves drilling accuracy in fractured or unstable formations.
2.High-Performance Design
– Carbide Button Configuration: Strategically placed tungsten carbide buttons for maximum impact energy transfer and extended bit life.
– Optimized Flushing Channels: Ensures efficient removal of cuttings and reduces balling in sticky formations.
3. Durability & Adaptability
– Manufactured from premium-grade alloy steel with advanced heat treatment for exceptional wear and impact resistance.
– Compatible with a wide range of rock types, including hard, abrasive, and highly fractured formations.
4. Easy Maintenance
Modular design allows for quick replacement of worn components, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Technical Specifications
– Drill Bit Diameter: 90mm to 350mm (custom sizes available).
– Connection Type: Standard API or custom thread options (e.g., R32, COP, etc.).
– Operating Pressure: 15–30 bar.
– Impact Frequency: 1,200–2,400 blows per minute (BPM).
– Material: High-strength steel body with tungsten carbide inserts.
Applications
– Mineral Exploration: Achieves high-quality core samples for accurate resource evaluation.
– Water Well Drilling: Efficiently penetrates hard rock layers while maintaining borehole stability.
– Geotechnical Surveys: Ideal for soil and rock sampling in complex geological conditions.
– Blast Hole Drilling: Enhances productivity in quarrying and mining operations.
Advantages Over Conventional DTH Bits
✅ Higher Penetration Rates: Optimized energy transfer ensures faster drilling.
✅ Cleaner Samples: Reverse circulation minimizes contamination for precise analysis.
✅ Reduced Air Loss: Sealed design prevents air leakage, improving energy efficiency.
✅ Extended Service Life: Robust construction reduces wear in abrasive environments.
Why Choose Our RC DTH Bit?
– Custom Solutions: Tailored designs to meet specific project requirements.
– Global Certifications: Compliant with ISO 9001 and international drilling standards.
– Technical Support: 24/7 expert assistance for troubleshooting and optimization.
Applications
RC tools are used in geological exploration, water well drilling etc


| Bit diameter | No.X Button diamater(mm) | Air hole | Weight (kg) | Hammer type | ||
| mm | inch | Gauge | Front | |||
| 115 | 41/2 | 8×14 | 4×14+4×13 | 2 | 10 | TH1080RC |
| 120 | 43/4 | 8×14 | 4×14+4×13 | 2 | 10.5 | TH1162RC |
| 127 | 5 | 8×14 | 4×14+4×13 | 2 | 11 | TH1186RC |
| 130 | 51/8 | 8×16 | 6×14+4×14 | 2 | 11.5 | TH1214RC |
| 133 | 51/4 | 8×16 | 6×14+5×14 | 2 | 15.6 | |
| 137 | 53/8 | 8×16 | 6×14+5×14 | 2 | 16.0 | TH1261RC |
| 140 | 51/2 | 8×16 | 6×14+5×14 | 2 | 18.8 | |
| 146 | 54/3 | 8×16 | 6×14+5×14 | 2 | 19.5 | TH1305RC |
| 152 | 6 | 8×16 | 6×14+5×14 | 2 | 21 | |
Notice: There is a chance that SHANDIKE may make changes on above-mentioned information. Product pictures and parameters about models, data, performances and specifications on this website are for reference only.
Shandike GSE DHD DTH Hammers
DTH (down-the-hole) drilling involves a drilling hammer at the bottom of a drill string, the hammer is powered by compressed air transmitted via drilling rod to drive piston and produce impact power, which is then delivered into rocks for drilling and crushing. DTH drilling can be applied in mining, quarrying, water well drilling, foundation piling, etc. DTH hammer uses compressed air to produce impact power, thus to drive drill bits to crush rocks.
• Premium material, fine CNC and heat-treatment manufacturing processes and optimized design;
• Good stability and reliability;
• High impact frequency;
• Lowered compressed air consumption;
• Long lifespan
Mining, quarrying, water well drilling, geothermal well drilling, foundation piling, etc.
 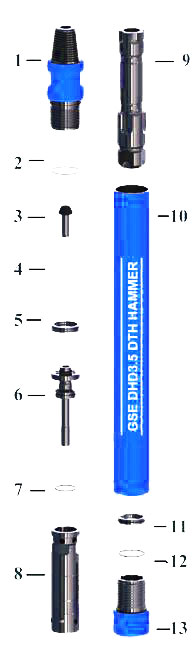 | 01 – Top Sub | 02 – O Ring | 03 – Check Valve | 04 – Spring |
| 05 – Steel Washer | 06 – Rigid Valve | 07 – O Ring | 08 – Internal Cylinder | |
| 09 – Pistion | 10 – Out Tube | 11 – Bit Retainer Ring | 12 – O Ring | |
| 13 – Drive Sub |
GSE-DHD3.5 DTH Hammer
| Net Weight | Out Diameter | GSE DHD3.5 DTH Hammer Length With Out Bits | Frequency at 18 Bar | |
| 22.62 kgs | 80 mm | 808 mm | 32 Hz | |
| Rec. Hole Size | Working Pressure | Air Consumption: M3(CBM)/min | ||
| 90 mm-105 mm | 8 bar – 30 bar | @10 bar | @18 bar | @24 bar |
| 4.5 | 9.5 | 12.5 | ||
GSE-DHD340 DTH Hammer
| Net Weight | Out Diameter | GSE DHD340 DTH Hammer Length With Out Bits | Frequency at 18 Bar | |
| 38.00 kgs | 99 mm | 881 mm | 31 Hz | |
| Rec. Hole Size | Working Pressure | Air Consumption: M3(CBM)/min | ||
| 108mm – 130mm | 8 bar – 30 bar | @ 10 bar | @ 18 bar | @ 24 bar |
| 5 | 10.2 | 15 | ||
GSE-DHD350 DTH Hammer
| Net Weight | Out Diameter | GSE DHD350 DTH Hammer Length With Out Bits | Frequency at 18 Bar | |
| 74.0 kgs | 126 mm | 1028 mm | 30 Hz | |
| Rec. Hole Size | Working Pressure | Air Consumption: M3(CBM)/min | ||
| 134mm – 152mm | 8 bar – 30 bar | @ 10 bar | @ 18 bar | @ 24 bar |
| 7.5 | 14.7 | 19.5 | ||
GSE-DHD360 DTH Hammer
| Net Weight | Out Diameter | GSE DHD360 DTH Hammer Length With Out Bits | Frequency at 18 Bar | |
| 112 kgs | 144 mm | 1135 mm | 28 Hz | |
| Rec. Hole Size | Working Pressure | Air Consumption: M3(CBM)/min | ||
| 154mm – 254mm | 8 bar – 30 bar | @ 10 bar | @ 18 bar | @ 24 bar |
| 8.7 | 14.5 | 25 | ||
GSE-DHD380 DTH Hammer
| Net Weight | Out Diameter | GSE DHD 380 DTH Hammer Length With Out Bits | Frequency at 18 Bar | |
| 180.0 kgs | 182 mm | 1228 mm | 23 Hz | |
| Rec. Hole Size | Working Pressure | Air Consumption: M3(CBM)/min | ||
| 203mm – 305mm | 8 bar – 30 bar | @ 10 bar | @ 18 bar | @ 24 bar |
| 12 | 26 | 35 | ||
Casing drilling, or casing while drilling (CWD) process, is a concept that combining two time-consuming processes, drilling and casing together, performing them at the same time. During the CWD process, powered by DTH hammer, a central piloting bit drives a ring bit to drill a hole wide enough for a casing tube to slide down, drilling and casing processes are therefore performed at the same time.
Eccentric is the most economical solutions because its ingenious reaming wing the bit is retrievable can be used at the next hole. This is particularly design for shallow holes, as is often the case in water well drilling, geothermal wells and for shallow micro-piling work. Odex is ideal for short holes in consolidated overburden. The component of Eccentric system consists of Pilot bits, Reamer bits, Guide device and casing shoe.
When drilling, the reamer bit will rotate out to enlarge the hole which enough for the casing tube slide down behind the reamer. When reached required depth, the drill pipe will drill to the reverse direction and the reamer bit will retract, it is allowing the whole drilling system to pass through the casing.
• Complete types of drilling tools suitable for casing tubes with various diameters;
• Good stability and reliability granted by premium alloy steel material and fine CNC manufacturing process;
• Cost-effectiveness realized by mass production.
Water well drilling, geothermal well drilling, foundation piling, geological prospecting, etc.
Structure
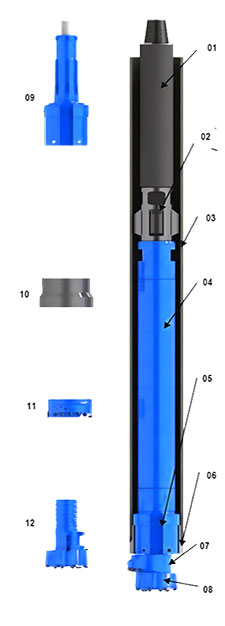 | 01 – Drill Pipe | 02 – Guide Sleeve | 03 – Steel Casing |
| 04 – DTH Hammer | 05 – Guide Device | 06 – Casing Shoe | |
| 07 – Reammer | 08 – Pilot Bit | 09- Guide Device | |
| 10 – Casing Shoe | 11 – Reammer | 12 – Pilot bit |
GSE-EDS82 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX82)
| GSE-EDS82 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX82) shank for IR3.5 DTH Hammer (other shanks are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may by used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 108 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 96 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 6 |
GSE-EDS90 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX90)
| GSE-EDS90 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX90) shank for DHD3.5 DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 115 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 102 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 6 |
GSE-EDS115A Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX115A)
| GSE-EDS115A Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX115A) Shank for IR DHD340A DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 142 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 128 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 7 |
GSE-EDS115B Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX115B)
| GSE-EDS115B Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX115B) Shank for DHD340 DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may be used: | |
| Manximum outside diameter (mm) | 146 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 130 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 8 |
GSE-EDS140 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX140)
| GSE-EDS140 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX140) Shank for IR DHD350R DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 168 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 152 |
| Wall thckness (mm) | 8 |
GSE-EDS145 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX145)
| GSE-EDS145 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX145) Shank for IR DHD350R DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 178 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 158 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 9 |
GSE-EDS147 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX147)
| GSE-EDS147 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX147) Shank for IR DHD350R DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casing may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 183 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 163 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 10 |
GSE-EDS165 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX165)
| GSE-EDS165 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX165) Shank for IR DHD360 DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 195 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 182 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 6.5 |
GSE-EDS180 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX180)
| GSE-ED180 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX180) Shank for DHD360, COP64, SD6 DTH Hammer | |
| Alternative casing may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 219 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 194 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 12.5 |
GSE-EDS190 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX190)
| GSE-EDS190 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX190) Shank for IR DHD360 DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 219 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 205 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 7 |
GSE-EDS230 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX230)
| GSE-EDS230 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX230) Shank for IR DHD380 DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 273 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 250 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 11.5 |
GSE-EDS240 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX240)
| GSE-EDS240 Eccentric Drilling System (ODEX240) Shank for IR DHD380 DTH Hammer (others are optional) | |
| Alternative casings may be used: | |
| Maximum outside diameter (mm) | 273 |
| Minimum inside diameter (mm) | 260 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 6.5 |
Retrac button bits are mainly used in loose rock mass with relatively broken rock. The retrac skirt design can assist in retrieving the drill tool, reduce the phenomenon of bit stuck and buried, and help improve the straightness of the borehole.
As a China retrac button bit supplier, we can provide you with high-quality button bit includes retrac rock drill bits, such as R25 retract button bit, R28 retract button bit, R32 retrac button bit, R35 retrac button bit, R38 retrac button bit, T38 retract drill bit, T45 retract drill bit, T51 retract drill bit, GT60 retract button bit, ST58 retrac button bit, ST68 retrac button bit, SR35 retrac drill bit and other types of rock drill bit.
R25
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 41 | 1 5/8″ | 5 × 9 | 2 × 8 | 2 | 1 | 0.78 | R25-417YFP |
| 45 | 1 3/4″ | 6 × 9 | 3 × 8 | 1 | 3 | 1 | R25-459YFP | |
| 48 | 1 7/8″ | 6 × 10 | 3 × 9 | 1 | 3 | 1.1 | R25-489YFP | |
| 51 | 2″ | 6 × 10 | 3 × 9 | – | 3 | 1.35 | R25-519YFP | |
| 55 | 2 11/64″ | 6 × 11 | 3 × 9 | 1 | 3 | 1.54 | R25-559YFP | |
| 57 | 2 1/4″ | 6 × 10 | 3 × 10 | – | 3 | 1.6 | R25-579YFP | |
| 64 | 2 1/2″ | 8 × 11 | 4 × 10 | 1 | 2 | 2.2 | R25-6412YFP | |
R28
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 45 | 1 3/4″ | 6 × 9 | 3 × 8 | 1 | 3 | 1 | R28-459YFP |
| 51 | 2″ | 6 × 10 | 3 × 9 | 1 | 3 | 1.35 | R28-519YFP | |
R32
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 45 | 1 3/4″ | 6 × 9 | 3 × 8 | 1 | 3 | 0.9 | R32-459YFP |
| 48 | 1 7/8″ | 6 × 10 | 3 × 9 | 1 | 3 | 1.1 | R32-489YFP | |
| 51 | 2″ | 6 × 10 | 3 × 9 | – | 3 | 1.2 | R32-519YFP | |
| 57 | 2 1/4″ | 6 × 10 | 3 × 10 | – | 3 | 1.7 | R32-579YFP | |
| 64 | 2 1/2″ | 6 × 11 | 3 × 10 | 1 | 2 | 2.2 | R32-649YFP | |
 | 60 | 2 23/64″ | 8 × 10 | 4 × 9 | 1 | 2 | 1.7 | R32-6012YFP |
| 64 | 2 1/2″ | 8 × 10 | 4 × 10 | 2 | 2 | 1.9 | R32-6412YFP | |
| 76 | 3″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 11 | 2 | 2 | 2.2 | R32-7612YFP | |
 | 76 | 3″ | 8 × 11 | 4 × 11, 1 × 11 | – | 4 | 3.3 | R32-7613YFA |
SR35
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 51 | 2″ | 8 × 9 | 3 × 9 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | SR35-5111YFP |
| 54 | 2 1/8″ | 8 × 9 | 3 × 9 | 2 | 1 | 1.8 | SR35-5411YFP | |
 | 54 | 2 1/8″ | 6 × 10 | 3 × 9 | 1 | 3 | 1.3 | SR35-549YFA |
R38
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 64 | 2 1/2″ | 8 × 10 | 4 × 10 | 2 | 2 | 1.9 | R38-6412YFP |
| 76 | 3″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 11 | 2 | 2 | 2.2 | R38-7612YFP | |
| 64 | 2 1/2″ | 6 × 11 | 3 × 10 | 1 | 2 | 1.9 | R38-649YFP | |
 | 64 | 2 1/2″ | 6 × 11 | 3 × 10, 1 × 9 | 1 | 2 | 1.9 | R38-6410YFA |
| 64 | 2 1/2″ | 8 × 10 | 4 × 10, 1 × 9 | 1 | 4 | 1.9 | R38-6413YFA | |
| 66 | 2 19/32″ | 6 × 11 | 3 × 10, 1 × 9 | 1 | 2 | 1.9 | R38-6610YFA | |
| 70 | 2 3/4″ | 8 × 10 | 4 × 10, 1 × 9 | 1 | 4 | 2.4 | R38-7013YFA | |
| 76 | 3″ | 8 × 11 | 4 × 11, 1 × 11 | – | 4 | 3.3 | R38-7613YFA | |
| 89 | 3 1/2″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 12, 2 × 10 | 1 | 4 | 5.3 | R38-8914YFA | |
| 89 | 3 1/2″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 11, 1 × 11 | 1 | 4 | 5.3 | R38-8913YFA | |
T38
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 64 | 2 1/2″ | 8 × 10 | 4 × 10 | 2 | 2 | 1.9 | T38-6412YFP |
| 76 | 3″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 11 | 2 | 2 | 2.2 | T38-7612YFP | |
| 64 | 2 1/2″ | 6 × 11 | 3 × 10 | 1 | 2 | 1.9 | T38-649YFP | |
 | 64 | 2 1/2″ | 6 × 11 | 3 × 10, 1 × 9 | 1 | 2 | 1.9 | T38-6410YFA |
| 64 | 2 1/2″ | 8 × 10 | 4 × 10, 1 × 9 | 1 | 4 | 1.9 | T38-6413YFA | |
| 70 | 2 3/4″ | 8 × 10 | 4 × 10, 1 × 9 | 1 | 4 | 2.4 | T38-7013YFA | |
 | 65 | 2 9/16″ | 6 × 12 | 4 × 10 | 1 | 2 | 3.1 | T38-6510YSP |
T45
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 76 | 3″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 11 | 2 | 2 | 2.2 | T45-7612YFP |
| 89 | 3 1/2″ | 8 × 13 | 5 × 12 | 2 | 2 | 5.2 | T45-8913YFP | |
| 102 | 4″ | 9 × 12 | 6 × 12 | – | 3 | 6.5 | T45-10215YFP | |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 9 × 14 | 7 × 13 | – | 3 | 10 | T45-11516YFP | |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 9 × 14 | 6 × 13 | – | 3 | 10 | T45-11515YFP | |
 | 76 | 3″ | 8 × 11 | 4 × 11, 1 × 11 | – | 4 | 3.2 | T45-7613YFA |
| 89 | 3 1/2″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 12, 2 × 10 | 1 | 4 | 5.4 | T45-8914YFA | |
| 102 | 4″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 12, 3 × 12 | – | 4 | 7.8 | T45-10215YFA | |
| 102 | 4″ | 8 × 13 | 4 × 12, 4 × 12 | – | 4 | 7.8 | T45-10216YFA | |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 8 × 14 | 4 × 13, 3 × 12 | – | 4 | 7.8 | T45-11515YFA | |
 | 76 | 3″ | 8 × 13 | 4 × 11, 1 × 11 | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | T45-7613YSA |
| 89 | 3 1/2″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 12, 1 × 12 | 1 | 4 | 4.7 | T45-8913YSA | |
T51
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 89 | 3 1/2″ | 8 × 13 | 5 × 12 | 2 | 2 | 4.6 | T51-8913YFP |
| 102 | 4″ | 8 × 14 | 7 × 12 | 1 | 2 | 7.1 | T51-10215YFP | |
| 102 | 4″ | 9 × 12 | 6 × 12 | – | 3 | 7.1 | T51-10215YFP1 | |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 9 × 14 | 7 × 13 | – | 3 | 10 | T51-11516YFP | |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 9 × 14 | 6 × 13 | – | 3 | 10 | T51-11515YFP | |
| 127 | 5″ | 9 × 14 | 7 × 13 | – | 3 | 13 | T51-12716YFP | |
  | 89 | 3 1/2″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 11, 1 × 11 | 1 | 4 | 5.3 | T51-8913YFA |
| 89 | 3 1/2″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 12, 2 × 10 | 1 | 4 | 5.4 | T51-8914YFA | |
| 102 | 4″ | 8 × 12 | 4 × 12, 3 × 12 | – | 4 | 7.8 | T51-10215YFA | |
| 102 | 4″ | 8 × 13 | 4 × 12, 4 × 12 | – | 4 | 7.8 | T51-10216YFA | |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 8 × 14 | 4 × 13, 3 × 12 | – | 4 | 7.8 | T51-11515YFA | |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 8 × 14 | 4 × 14, 3 × 12 | – | 4 | 7.8 | T51-11515YFA1 | |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 8 × 14 | 4 × 14, 4 × 12 | – | 4 | 10 | T51-11516YFA | |
 | 89 | 3 1/2″ | 9 × 11 | 3 × 11, 2 × 10 | 1 | 3 | 4.8 | T51-8914YFA2 |
| 102 | 4″ | 9 × 12 | 3 × 12, 3 × 11 | 1 | 3 | 6.9 | T51-10215YFA1 | |
| 110 | 4 21/64″ | 9 × 14 | 6 × 12, 2 × 11 | – | 3 | 10 | T51-11017YFA | |
| 127 | 5″ | 8 × 16 | 4 × 14, 4 × 14 | – | 4 | 13.5 | T51-12716YFA | |
 | 102 | 4″ | 8 × 14 | 4 × 13, 1 × 13 | – | 2 | 10.1 | T51-10213YSA |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 9 × 14 | 6 × 12, 4 × 12 | – | 3 | 9.45 | T51-11519YSA | |
GT60
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 92 | 3 5/8″ | 9 × 12 | 9 × 12 | – | 2 | 5.1 | GT60-9218YSP |
| 96 | 3 25/32″ | 9 × 12 | 9 × 12 | – | 2 | 6.5 | GT60-9618YSP | |
| 102 | 4″ | 9 × 13 | 10 × 12 | – | 2 | 8.5 | GT60-10219YSP | |
 | 115 | 4 1/2″ | 9 × 14 | 10 × 12 | – | 3 | 10.8 | GT60-11519YSP |
| 127 | 5″ | 9 × 16 | 10 × 14 | – | 3 | 15 | GT60-12719YSP | |
| 140 | 5 1/2″ | 9 × 16 | 10 × 14 | – | 3 | 15 | GT60-14019YSP | |
| 152 | 6″ | 9 × 16 | 12 × 16 | – | 3 | 20 | GT60-15221YSP | |
 | 115 | 4 1/2″ | 9 × 16 | 6 × 13 | – | 3 | 15 | GT60-11515YSP |
ST58
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 89 | 3 1/2″ | 10 × 12 | 4 × 12, 2 × 12 | – | 4 | 5 | ST58-8916YSA |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 10 × 14 | 4 × 14, 4 × 14 | – | 4 | 10 | ST58-11518YSA | |
ST68
| Appearance | Diameter | Buttons | Flushing Hole | Weight | Model No. | |||
[mm] | [in] | Gauge [No.] × [mm] | Front [No.] × [mm] | Side [No.] | Front [No.] | [kg] | ||
 | 102 | 4″ | 10 × 12 | 4 × 12, 4 × 12 | – | 4 | 9.3 | ST68-10218YSA |
| 115 | 4 1/2″ | 10 × 14 | 4 × 14, 4 × 14 | – | 4 | 10 | ST68-11518YSA | |
Hand-held Rock Drill is widely used for dry drilling in the medium-hard and hard rock. It is widely used in metallurgy, coal,railway, transportation, water conservancy construction and national defense stone works, etc. It is suitable for drilling andblasting under various of rocks at any direction angles.

Advantage
Tapered drill rod,another name called taper rod, tapered drill steels, This provides a hexagonal chuck section to provide leverage for the rotation chuck bushing. It usually has a forged collar to maintain the proper shank striking face position in the rock drill, and a tapered bit end. Tapered steel lengths available from 0.6 mto 3.6 m in length—are measured from the collar to the bit end.

| Hand held rock drill specification | |||||
| Type | Y20LY | Y24 | Y26 | Y19A | TY24C |
| Weight(kg) | 18 | 23 | 26 | 19 | 23 |
| Shank size(mm) | 22*108 | 22*108 | 22*108 | 22*108 | 22*108 |
| Cylinder dia(mm) | 65 | 70 | 75 | 65 | 67 |
| Piston stroke(mm) | 60 | 70 | 70 | 54 | 70 |
| Working pressure(mpa) | 0.4 | 0.4-0.63 | 0.4-0.63 | 0.4-0.5 | 0.4-0.63 |
| Impact frequency(hz) | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| Air consumption | 25 | 55 | 47 | 37 | 55 |
| Air pipe inner dia(mm) | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| Rock drill hole dia(mm) | 30-45 | 30-45 | 30-45 | 30-45 | 30-45 |
| Rock drill hole depth(m) | 3 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
1、The height of the machine is moderate and the range of the stroke is large, so it can drill the anchor holes which are perpendicular to the roof surface, which solves the problem that the anchor holes in the roadway are not perpendicular to the surface of the roof for a long time, which guarantees the quality and progress of the project, saves the construction cost and improves the efficiency.
2、Good comprehensive rock drilling performance, not only for medium hard rock drilling, but also for rock drilling with f≤6, which can be applied to both rock roadway and quasi roadway.
3、Simple structure and more durable, easy to maintain, lower maintenance cost
4、Flexible start, air and water linkage, air leg fast return, air pressure adjustment and other institutions.
5、The control handle is concentrated with the shank body, the mechanism is novel and convenient to operate with the muffler cover can effectively reduce the noise and change the direction of the row of visits at will to improve the site The operation conditions of the field
6、YT28 rock drill is suitable for wet rock drilling of medium hard or hard rock.

Tunneling and support in mining, transportation, water conservancy, hydropower and other projects. It is mainly used for quarries – dividing rocks.


| Weight | kg | 28 |
| Size | mm | 670 |
| Working pressure | Mpa | 0.5~0.63 |
| Piston diameter | mm | 80 |
| Piston stroke | mm | 60 |
| Air pipe inner diameter | mm | 25 |
| Water pipe inner diameter | mm | 13 |
| Drilling diameter | mm | 34~45 |
| Max drilling depth | m | 5 |
| Shank size | mm | H22×108 |
| Impact frequency | Hz | ≥37 |
| Impact energy | J | ≥70 |
| Air consumption | L/s | ≤81.6 |
YN27C type internal combustion rock drill is widely used in mining, road construction, quarrying, national defense engineering, etc., with various functions of splitting, crushing, tamping and chipping for mining, cement road surface and asphalt road surface.

YN27C internal combustion rock drill has the functions of drilling, splitting, crushing, ramming, shoveling and so on. It can drill holesin rock vertically down, horizontally down to less than 45° and vertically down to the deepest 6 meters. YN27C is widely used in mining, road construction, quarrying, national defense engineering, etc.

| model | YN27C | Deepest drilling depth | >6M |
| The host weight | 27 kg | Fuel tank capacity | ≥1.14L |
| Carburetor type | No float type | The borehole speed | ≥250MM/MIN |
| engine type | gasoline engine | Ratio | 12° 1 |
| sparking mode | SR contactless system | Spark plug electrodega | 0.5-0.7MM |
| engine capacity | 185cm3 | Oil consumption rate | <0.12L/M |
| Legal and load speed | ≥2450r/min | Striking energy | >25J |
| Iron idling speed | >200r/min | The borehole diameter | 26-46 (MM) |
| Iron shank size bit rod | 22x108mm | Iron shank size bit rod Hexagon | 22 x108mm |
1.YT24 is suitable for drilling horizontal or tiptilted blasthole in solid hard rocks as well as vertical bolt holes on the roof.
2.YT24 can be used with the air leg FT140B, FT140BD. It is also installed on drill rig or drill frame; meanwhile, we provide a transparent lubricator FY200B to observe the oil level and adjust the oil quantity in order to make sure a favorable lubrication.
3. It is the indispensable tool in mining, railway, transportation, water conservancy construction and earthwork projects.


| Weight | kg | 24 |
| Size | mm | 675 |
| Working pressure | Mpa | 0.4~0.63 |
| Piston diameter | mm | 70 |
| Piston stroke | mm | 70 |
| Air pipe inner diameter | mm | 19 |
| Water pipe inner diameter | mm | 13 |
| Drilling diameter | mm | 34~42 |
| Max drilling depth | m | 5 |
| Shank size | mm | H22×108 |
| Impact frequency | Hz | ≥31(0.5MPa) |
| Impact energy | J | ≥31(0.5MPa) |
| Air consumption | L/s | ≤52 |
| Rotation | r/min | 250 |
Drill rod threads are divided into several main types, including square threads, taper pipe threads, spiral threads, and straight threads. These threads have their own unique characteristics and are suitable for different drilling conditions and requirements. The selection of thread type depends on factors such as the diameter of the drill rod, the material to be drilled, the drilling depth, and the torque required. It is recommended to consult professionals or manufacturers for specific selection advice to ensure that the drill rod threads meet the needs of the project.

YT29A air-legged rock drills are heavy-duty push-leg (air-legged) rock drills with low energy consumption, which are more suitable for drilling horizontal or inclined holes in medium-hard and hard (f=8-18) rocks, as well as drilling anchor holes upwards or downwards. It can be used with FT160A (or FT160B, 160C) according to the size of the roadway section and operating conditions, and can also be used with the drill truck or drill frame for dry or wet rock drilling. In addition, our company provides all YT29A rock drill parts as follows: piston, rotating sleeve, spiral rod, brass nut, valve set, ratchet, tower spring, manipulation valve, shank body, cylinder body, main body, brazing sleeve, brazing card, brazing card bolt, oiler, water injection valve body, fastening pin, ratchet pawl, air pipe nut, air pipe elbow, water needle, etc.

1、More output power
2、Rock drilling speed is faster
3、Super strong lubrication system to ensure the long time operation of movement parts
4、The whole machine has optimized design, the impact energy and impact frequency have reached an excellent match, it is your ideal rock drilling tool.
5、Gas and water linkage, quick return of the gas leg, air pressure adjustment and other institutions.
6、Control handle centralized with Back head, the mechanism is novel and convenient to operate, the muffler cover can effectively reduce the noise and change the direction of discharge at will to improve the working conditions in the field.Field operating conditions

Mining, traffic, tunnels, water conservancy construction, quarries and other work
1、Check the integrity and rotation of all parts (including rock drill, bracket, or rock drill cart) before drilling, fill necessary lubricant, and check whether the wind and waterways are smooth and whether the connection joints are firm.
2、Knock on the roof near the working face, i.e. check whether there are live rocks and loose rocks on the roof and second gang near the working face, and make necessary treatment.
3, the working surface of the flat shell hole location, is to be pounded flat in advance before allowing rock drilling, to prevent slippage or shell hole displacement.
4. It is strictly forbidden to drill dry eyes, and we should insist on wet rock drilling, turn on the water first and then the wind when operating, and turn off the wind and then the water when stopping drilling. When opening the hole, run at low speed first, and then drill at full speed after drilling to a certain depth.
5、No gloves are allowed to be worn by the drillers when drilling.
6、When using the air leg to drill the hole, pay attention to the standing posture and position, never rely on the body to pressurize, let alone stand in front of the rock drill under the work brazing rod, to prevent injury from broken brazing.
7、If abnormal sound and abnormal water discharge are found in rock drilling, stop the machine for inspection and find out the reason and eliminate it before continuing to drill.
8、When withdrawing from the rock drill or replacing the brazing rod, the rock drill can run slowly and pay attention to the position of the rock drill braze.
| Weight | kg | 27 |
| Size | mm | 659 |
| Working pressure | Mpa | 0.4~0.63 |
| Piston diameter | mm | 82 |
| Piston stroke | mm | 60 |
| Air pipe inner diameter | mm | 25 |
| Water pipe inner diameter | mm | 13 |
| Drilling diameter | mm | 34~45 |
| Max drilling depth | m | 5 |
| Shank size | mm | H22×108 |
| Impact frequency | Hz | ≥37(0.5MPa) |
| Impact energy | J | ≥69(0.5MPa) |
| Air consumption | L/s | ≤65 |
| Rotation | r/min | 300 |
Regular maintenance and proper handling of screw drilling tools can help extend their lifespan and ensure optimal performance. Here are some tips for maintaining and maintaining screw drilling tools during use:
1. Clean the tools after each use: Use a soft cloth or brush to remove any debris or dust from the tool. This will reduce the risk of damage or rusting.
2. Lubricate the tools: Apply a small amount of lubricant to the tool’s threads, shank, and cutting edges. This will help to reduce friction and prevent the tool from getting stuck or breaking.
3. Store the tools properly: Keep the tools in a dry place, away from moisture or humidity. Store them in a protective case or wrap them in a clean cloth to prevent damage or corrosion.
4. Inspect the tools regularly: Check the tools for signs of wear or damage, such as dulling or chipping of the cutting edges or threads. Replace any damaged parts immediately.
5. Handle the tools carefully: Avoid dropping or striking the tools, as this can cause damage or deformities to the tool.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your screw drilling tools are well-maintained and perform optimally during use.

Using laser cleaners requires careful attention to safety and operational considerations. Here are some precautions to take when using laser cleaners:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses with the correct optical density for the laser wavelength being used. Depending on the laser power and the specific cleaning environment, additional PPE such as gloves, face shields, and protective clothing may be necessary.
Area Preparation:
Ensure that the cleaning area is properly prepared and free of flammable materials or other hazards that could be ignited by the laser beam or the cleaning process.

Ventilation:
Provide adequate ventilation to remove any fumes, vapors, or particulates generated during the cleaning process. This helps maintain a safe working environment and prevents exposure to potentially harmful substances.
Controlled Access:
Restrict access to the laser cleaning area to authorized personnel only. Use signage and barriers to clearly demarcate the laser operation zone and prevent unauthorized entry.
Training:
Ensure that operators are properly trained in the safe use of laser cleaners, including how to operate the equipment, handle laser hazards, and respond to emergencies. Regular training updates and refresher courses are also beneficial.
Beam Control:
Use beam control mechanisms such as beam shutters, interlocks, and beam blocks to prevent accidental exposure to the laser beam. Ensure that the laser beam is directed away from reflective surfaces and bystanders.
Monitoring:
Continuously monitor the laser cleaning process and the surrounding environment for any signs of abnormal operation, such as smoke, unusual odors, or unexpected reflections of laser light.
Emergency Procedures:
Establish clear procedures for responding to emergencies, including laser beam exposure, fire, chemical spills, or other accidents. Provide appropriate emergency equipment such as fire extinguishers, eye wash stations, and first aid kits.
Maintenance:
Perform regular maintenance and inspections of the laser cleaning equipment to ensure proper functionality and safety. Follow manufacturer recommendations for calibration, alignment, and servicing.
Regulatory Compliance:
Adhere to relevant safety standards and regulations governing the use of lasers in your jurisdiction, such as ANSI Z136.1 in the United States or IEC 60825 internationally. Obtain any necessary permits or approvals for operating laser equipment.
By following these precautions and implementing proper safety measures, you can minimize the risks associated with using laser cleaners and create a safe working environment for operators and bystanders.
January 11, 2024
January 11, 2024